Introduction
Marketing measurement is a big problem, but the solution to the problem doesn’t also have to be big. In fact, it can be small.
This month’s post is about taking a small data approach to a big marketing problem.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
On Monday afternoon, I met my friend Reuben to get caught up over a coffee. I always enjoy our chats as they usually cover a wide range of interesting topics. Reuben also tends to ask great questions and make insightful comments. Monday was no exception.
While discussing how pervasive technology, analytics and big data are in marketing, we concluded that in contrast to all of that complexity and big data, I come at marketing measurement from a different angle; with something we might call a small data approach.
There is an emerging definition of small data as the few key pieces of meaningful, actionable information that we can uncover by analyzing big data. Those insights you extract from your big data become the last steps along the way to making better marketing decisions.
Actually, neither one of us had that definition of small data in mind during our discussion. Rather, we spoke of my “small data” approach to marketing measurement as small relative to other approaches and to the complexity of the problem.
My approach does align with the above definition of small data in the sense that I am very focused on organizing the chaos of all that data, uncovering insights and helping marketers to learn what they need to know so they can make better decisions. That is the reason to measure marketing and it needs to be the focus of any approach to measuring marketing.
Where my scorecard-based approach might also seem a bit contrarian is in its emphasis on measuring results vs. objectives and in not trying to calculate a financial return on investment (ROI). Although it would be ideal to accurately measure the financial ROI of marketing programs, as I have written about in the past, I think there are too many problems with doing financial ROI calculations for individual marketing programs.
I’ve always thought of my approach as a practical approach to a complex problem. As of Monday afternoon, I’m also starting to think about it as a small data approach to a big data problem. To explain what I mean by a small data approach, let me start with some thoughts on big data.
Big Data
Big data flows out of a set of circumstances that will tend to occur at bigger companies, and might include some combination of the following:
- Big marketing budgets
- Many marketing programs
- Many products and/or services
- Many communications channels
- Many and diverse customers and customer segments
- Many touch points on the customer path-to-purchase
- Many transactions
These circumstances lead to a whole lot of data to analyze and understand which in turn leads to big data measurement solutions that will also tend to be big, complex, sophisticated and expensive.
With all the buzz around big data, it is easy for small and mid-sized companies to conclude that a high-science, big data solution must be the only legitimate way to approach marketing measurement. For many of these companies, a big, costly sophisticated approach isn’t needed or practical under their circumstances. A smaller, more practical approach can do the trick.
Small Data
Most small to mid-sized companies don’t operate under the same set of circumstances. Their budgets aren’t as big, their marketing activity is much less involved, their world is much less complex and they generate and collect a smaller amount of data. They also have fewer resources with which to take on the problem that all marketers must solve, which is to determine the best ways to invest their budgets.
A small data approach can be a great fit under these smaller circumstances. Yet, given the range of company size and marketing activity within the small to medium sized businesses segment, a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work. Any approach needs to have some built in flexibility so you can scale up or down to be appropriate for the size of the marketing budget being measured.
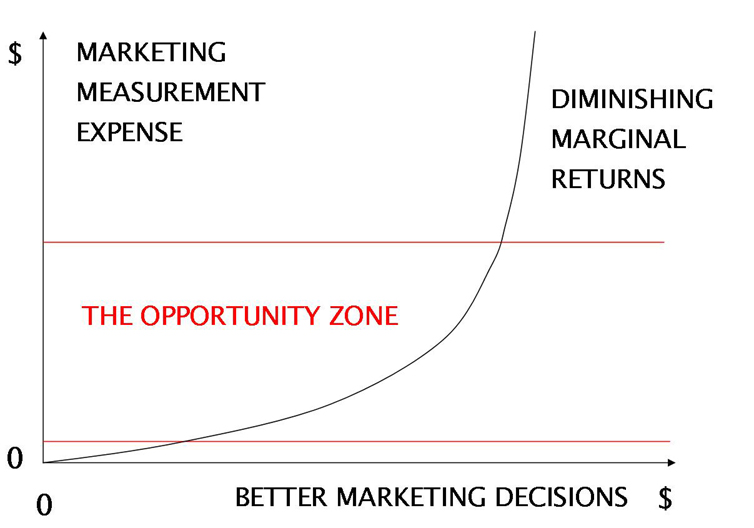
That’s really where I stand on marketing measurement. Right size your approach to your circumstances, and don’t overspend on measurement by bringing an over-sized solution to your problem.
Don’t over allocate resources to measuring something that you can’t measure perfectly, as the law of diminishing marginal returns will ensure you waste some of those precious resources. This is not about measuring perfectly; it’s about perfecting your marketing.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
About the Author: Rick Shea is President of Optiv8 Consulting, a marketing effectiveness consultancy with a focus on helping small to mid-sized organizations measure their marketing so they can stop wasting money.
Copyright ©2014 Optiv8 Consulting. All rights reserved.
You may reproduce this article by including this copyright and, if reproducing electronically, including a link to: http://www.optiv8.com/